Genetic study of the live vaccine could help efforts toward eradication.
2:20 PM
Author |
While the world reels from the spread of SARS-CoV2, the new coronavirus behind COVID-19, a much older and previously feared scourge—poliovirus—is close to being completely eradicated. The polio vaccines, developed by Jonas Salk and Albert Sabin in the mid-1950s, heralded the elimination of polio from the U.S., saving countless children from sudden paralysis and death. In the developing world, however, outbreaks of poliovirus still occur sporadically, an ironic consequence of the polio vaccine itself.
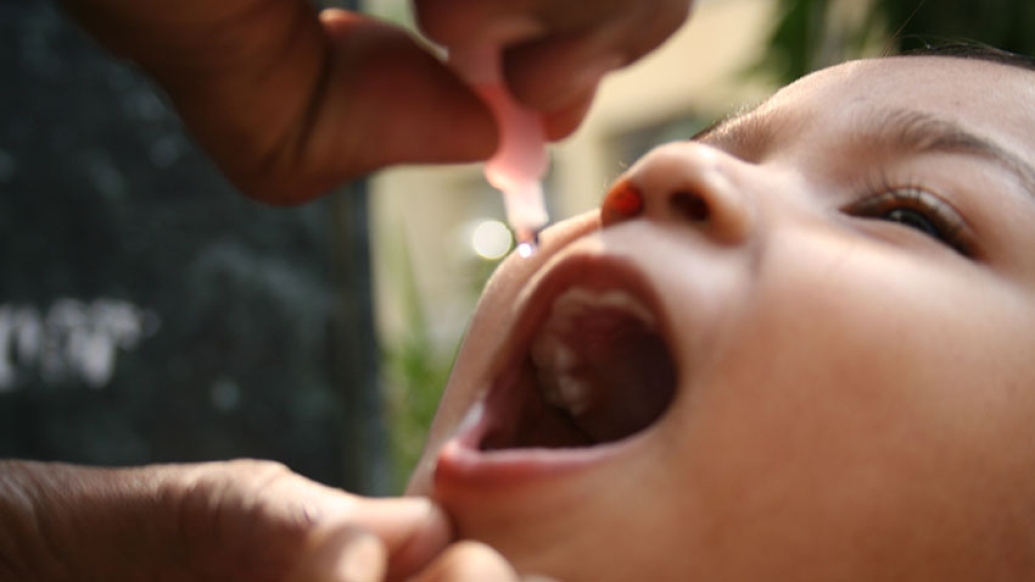
The polio vaccine comes in two types: the Salk vaccine, made with a killed virus and the Sabin vaccine, made with a live but weakened, or attenuated, virus. The Sabin vaccine has several advantages for use in the developing world, including the fact that it does not need to be kept cold, and as an oral vaccine, it does not require needles. However, because it contains a live, albeit weakened polio virus, that virus is able to evolve into more virulent forms and cause outbreaks months to years following a vaccination campaign.
In a new paper, Adam Lauring, M.D., Ph.D., of the department of microbiology & immunology and the division of infectious disease and a collaborative team describe an enterprising study that allowed them to view the evolution of the vaccine virus into a more dangerous form in real time.
"Most outbreaks of type 2 polio virus are caused by the vaccine. Then you have a problem where our best weapon is that same vaccine, so you're kind of fighting fire with fire," says Lauring.
Like Podcasts? Add the Michigan Medicine News Break on iTunes or anywhere you listen to podcasts.
In an effort to understand the basic biology of poliovirus and how it replicates, Lauring's lab seized an opportunity to build on an earlier study of a new vaccination campaign in semi-rural Bangladesh. This study, which was run by Mami Taniuchi, Ph.D., of the University of Virginia and Michael Famulare, Ph.D,. of the Institute for Disease Modeling in Seattle, Washington, along with a team from the International Centre for Diarrhoeal Disease Research, Bangladesh, followed households where children were vaccinated with the live attenuated virus, collecting weekly stool samples from each household member. The virus within those samples was then genetically analyzed.
"There's a lot of work being done to try and understand how the virus goes from attenuated to virulent again," says Lauring. "What we haven't known is what it is doing in those first few weeks or months. This was an opportunity to see those early steps."
SEE ALSO: Flu Virus Evolution Can Be Unexpectedly Slow and Inefficient
The team was able to confirm three critical mutations that were inferred by previous investigators to be necessary for the virus to become virulent again, identifying for the first time the rate of mutation for those genes from week to week. They also discovered that the attenuated polio virus evolves extremely quick within hosts; much faster than what is typically seen with other viruses over these short timescales.
"There were a lot of mutations that were being selected because they helped the virus be a better virus," says Lauring. He notes that this could be a critical insight for disease surveillance purposes. Sewage could be analyzed for signs of these types of mutations, serving as an early warning system of a potential outbreak.
MORE FROM THE LAB: Subscribe to our weekly newsletter
The work also revealed a spot of good news: while the virus excelled at evolving within a person, those changes were not easily transmitted from person to person.
"For all the evolution that happens in a person, transmission tends to put a brake on that and really slows things down," says Lauring.
Yet every now and then, an enhanced virus makes it to a new host and gains a foothold, triggering disease. The hope, explains Lauring, is that this work will "inform in a better way to tinker with the vaccine so you get fewer downsides and still maintain its upsides—that it's actually a very effective vaccine."
This study was supported by grants from the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation and the Burroughs Wellcome Fund.
Paper cited: "The early evolution of oral poliovirus vaccine is shaped by strong positive selection and tight transmission bottlenecks," Cell Host & Microbe. DOI: 10.1016/j.chom.2020.10.011

Explore a variety of healthcare news & stories by visiting the Health Lab home page for more articles.

Department of Communication at Michigan Medicine
Want top health & research news weekly? Sign up for Health Lab’s newsletters today!