Sherburne is a Senior Public Relations Representative with Michigan News, covering social research and physical sciences. She previously worked as a reporter in Petoskey, Michigan and as a science writer for University of Florida Health before joining U-M.


Health Lab
New study measured continuous heart rate, step count, sleep data and daily mood scores. The researchers also estimated circadian time and time awake from minute-by-minute wearable heart rate and motion measurements.
Health Lab
People were plunged into the issue of COVID-19

Health Lab
Alzheimer’s disease and other forms of dementia, and the mild cognitive impairment that can precede these conditions, now affect one-third of Americans over age 65.

Health Lab
Legality and cultural shifts could be behind change, says expert
Health Lab
Researchers track protein binding, build synthetic proteins to study gene expression.

Health Lab
Your neighborhood is more impactful than you think when it comes to your social emotional health.

Health Lab
According to a study, researchers find that disrupted sleep in mice leads to limited to no emotional responses.
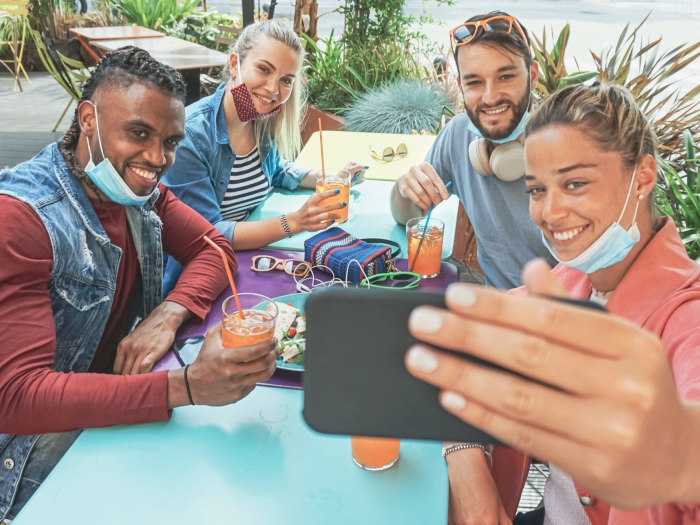

Health Lab
While nearly all Americans use a mask at some point each week, very few consistently wear their mask during many common potentially risky activities, study shows.