Miss a workout? No big deal. But two weeks away from the gym can mean declines in strength, stamina and health, even for the ultrafit.
7:00 AM
Author |
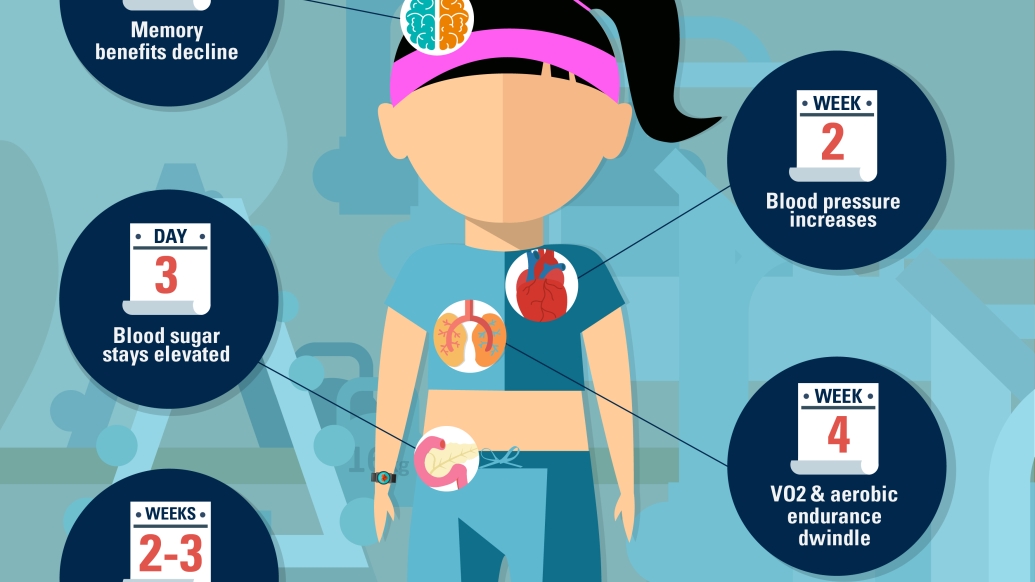
When it comes to exercise, consistency is key.
Even for the fittest among us, a few weeks away from training can result in rapid declines in strength, aerobic capacity and the biomarkers, such as blood pressure, that indicate a healthy body.
SEE ALSO: Tips for Treating and Preventing ACL Injuries in Everyday Athletes
"Detraining will occur relatively quickly, with major declines occurring after two or three weeks," says Mark Peterson, Ph.D., an assistant professor of physical medicine and rehabilitation at the University of Michigan. The graphic above outlines some of the changes and when they occur.
But maintaining a regular exercise routine has many benefits.
"Strength preservation and daily physical activity in adolescence, midlife and older adulthood are powerful protective factors for maintaining cardiovascular health and functional mobility, reducing injury and extending life expectancy," Peterson says.
Below, Peterson offers tips for sticking with an effective exercise routine.
-
Aim for intermittent physical activity. Break up exercise into chunks throughout your day. It's effective and fits around busy schedules.
-
Go gym-free. Resistance exercise can take place without access to a gym. Simply use your body weight for moves such as body weight squats, push-ups, planks, pull-ups (or inverted rows), lunges, stair climbing or even playing in a jungle gym.
-
Combine forces. Aerobic and resistance exercise together are far superior to either alone for improving body composition and metabolic health, increasing muscle strength and endurance and enhancing cardiorespiratory health and fitness.
-
Try HIIT. Occasional high-intensity interval training (HIIT) can be used to improve health and fitness in less time. Cycling, running or stair-climbing HIIT for equivalent work and rest ratios can produce immediate and large effects.
-
Get outdoors. Regular participation in exercise and recreation outdoors can reduce stress and depressive symptoms, improve mood and enhance cognitive health.
Graphic Sources: "Lowering Physical Activity Impairs Glycemic Control in Healthy Volunteers," Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise; "The Relationship between the Blood Pressure Responses to Exercise following Training and Detraining Periods," PLOS One; Iñigo Mujika, Ph.D., Outside Online; University of Copenhagen/Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine; University of Sao Paulo/New York Times Well Blog; "Effects of detraining on endurance capacity and metabolic changes during prolonged exhaustive exercise," Journal of Applied Physiology.

Explore a variety of health care news & stories by visiting the Health Lab home page for more articles.

Department of Communication at Michigan Medicine
Want top health & research news weekly? Sign up for Health Lab’s newsletters today!





