Research and Policy Media Relations Manager
Gavin draws on more than 25 years of experience in communicating about science, medicine and health policy. She focuses mainly on the health services research done by members of the U-M Institute for Healthcare Policy and Innovation, who work to understand and improve the safety, quality, equity and affordability of health care. As part of the Michigan Medicine communication team, she has lead responsibility for primary care and mental health topics. Contact: [email protected]; Twitter: @Karag


Health Lab
Proven sleeping habits that can help older people foster healthy sleep without relying on medicines or supplements, which pose real risks as people get older

Health Lab
Americans nearing retirement face double trouble: more disability and cognitive issues than their elders had at this age and a longer wait to collect Social Security.

Health Lab
A new national poll finds that many people 65 and older take prescription sleep aids — even though guidelines warn against it. What the findings mean for patients and providers.

Health Lab
A discovery in hormone-producing cells could lead to a better understanding of diseases related to misfolded proteins.

Health Lab
Read the latest results from a new study on diabetes treatment which found that many older adults with diabetes are dangerously overtreated.

Health Lab
A new understanding of the interaction among multidrug-resistant bacteria, and how antibiotics affect them, could lead to better infection prevention.
Health Lab
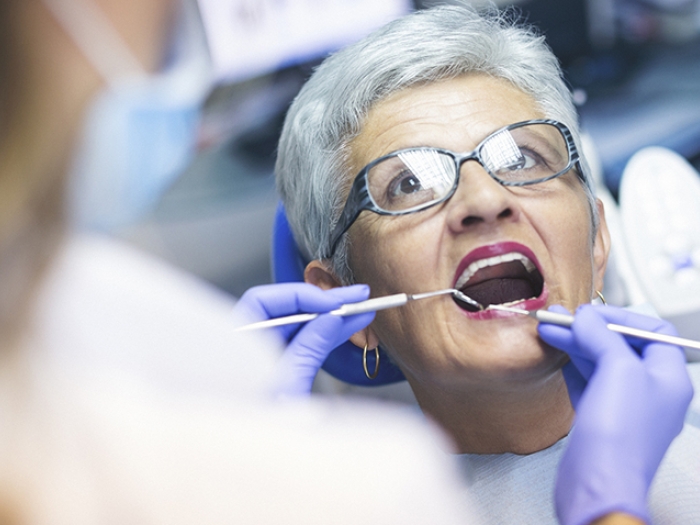
Regular dental care can help prevent oral health issues such as tooth decay and infections. Take advantage of free and low cost options for proper dental care
Health Lab
A new poll finds widespread oral health issues among people in their 50s and early 60s, especially among those who lack dental insurance.

Health Lab
Read results from a new study on the 'pop drop phenomenon', and learn how caregiver fatigue, stress and burnout results in increased healthcare costs.

Health Lab
Coronary artery bypass expenses vary widely across hospitals, a new study finds. Addressing a few key areas could lower hospital bills and improve quality of care.

Health Lab
Read how pheromones and attraction happen between male and female fruit flies, and how pheromones, fertility and mating are connected. This research could help us understand human attraction.

Health Lab
A federal “right-to-try” law for medical treatments could soon become reality. But systems to expand access to investigational options while protecting patients are already in place, says a U-M expert.

Health Lab
New U-M research shows that pluripotent stem cells can grow into structures similar to amniotic sac. See how this discovery could aid infertility research.

Health Lab
Get the latest information about bone marrow's role in HIV, and learn out how these findings could lead to new treatments and cures for HIV.

Health Lab
A study of DNA from prehistoric German dogs yielded new clues about how dogs became domesticated from wolves. The same techniques can teach us about our own ancient origins — and diseases that affect both species.