Lead Research Communicator
Malcom is a lead research communicator for Michigan Medicine and research communications strategist for the U-M Medical School, with more than 20 years of experience in strategic communications, marketing, and health and science writing. She covers the basic science departments, pulmonary and critical care medicine, infectious disease, pathology and anesthesiology. Contact: [email protected]


Health Lab
The CDC’s recent reframing for measuring COVID-19 risk levels has led to changed guidance for mask wearing. The move has left many wondering how to navigate a world where the COVID pandemic is not quite over but is trending toward becoming endemic.

Health Lab
New study provides insights into how the microbiome processes seaweed.
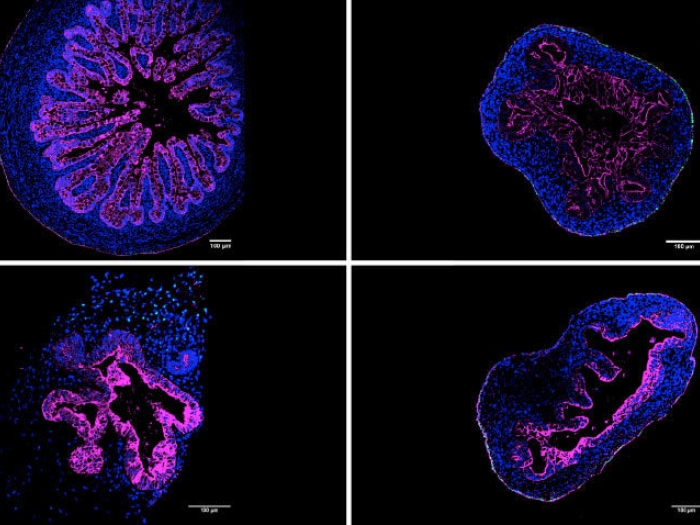
Health Lab
Researchers successful generate organoids in suspension, offering a new opportunity for researchers.

Health Lab
Misinformation about COVID has spread in tandem with the virus and its variants. Michigan Medicine experts debunk myths about COVID vaccines, testing, illness, treatments and more.

Health Lab
Prescribing of drugs associated with C. diff infection and antibiotic-resistant pathogens.
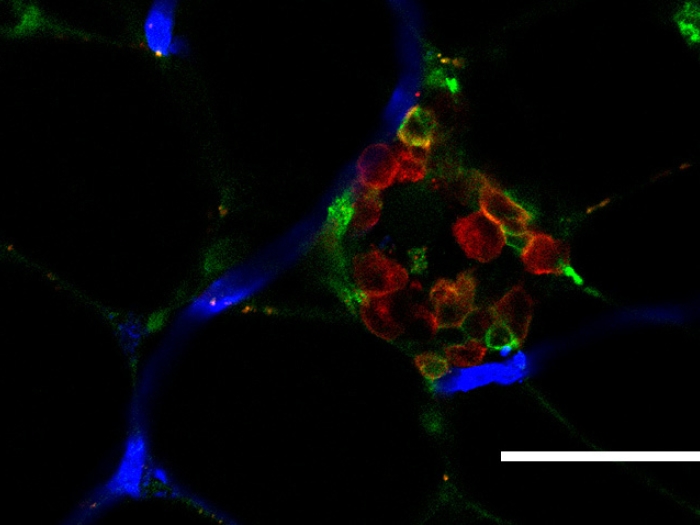
Health Lab
Clues suggest anti-inflammatory macrophages are different in people with diabetes.
Health Lab
With the ballooning cases of COVID worldwide, an expert looks at what is known about the Omicron variant.

Health Lab
Enhanced research tool is a potential boon for research in genetic diseases and developmental biology.
Health Lab
The size of a microbiome sample from rectal swabs varies from patient to patient and can predict infection risk.
Health Lab
The discovery reveals how bacteria silence potentially deadly genes.
News Release
Four Michigan universities will receive $18.5 million in federal funds over the next two years to collect and analyze genomic data to address emerging infectious disease threats and enhance the state’s ability to respond to those threats, announced the Michigan Department of Health and Human Services (MDHHS) today.
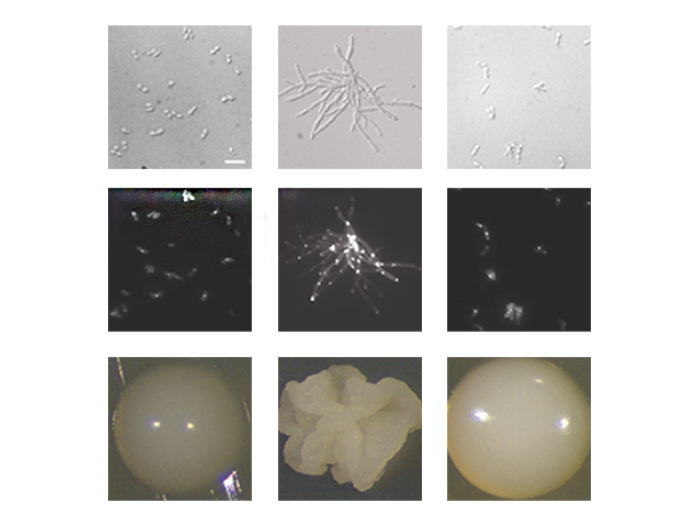
Health Lab
A newly developed tool is studying the genetics underlying the emerging fungal pathogen, Candida auris.

Health Lab
Celebrating another holiday season during COVID means that safety guidelines continue to be crucial. Four expert-approved tips for reducing the risk of infection and illness.
News Release
In early 2020, as Michigan Medicine faculty, learners and staff turned their attention to halting the spread of COVID-19 and providing much-needed care for patients, they also ramped up research efforts to include studies dedicated to understanding the novel coronavirus, SARS-CoV2 and the effects of COVID-19.
Health Lab
CRISPR technology is helping researchers study fat cells, and the method could revolutionize the process and cost of developing mouse models for lab research.