Public Relations Representative
Fromson joined Michigan Medicine in March 2021. He covers the neurosciences and cardiovascular medicine. He spent three years as a television reporter in West Michigan and is passionate about multimedia storytelling. Contact: [email protected] Twitter: @noahfromson


Health Lab
People with higher levels of metals found in their blood and urine may be more likely to be diagnosed with — and die from — amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, or ALS, a University of Michigan-led study suggests.

Health Lab
More than two-thirds of those people take a type of blood thinner called a direct oral anticoagulant. These DOACs, such as rivaroxaban (brand name Xarelto) and apixaban (brand name Eliquis), are under- or over-prescribed in up to one in eight patents. These prescribing issues can have life-threatening consequences, and they most often occur after a provider writes the initial prescription, according to a study led by Michigan Medicine.

Health Lab
A study found personalized text messages effectively promoted increased physical activity for patients after significant heart events — such as a heart attack or surgery — but those effects later diminished.

Health Lab
A study led by Michigan Medicine narrows in on the cumulative effects of years of high systolic blood pressure — the top number on the blood pressure reading and how hard the heart pumps blood to the arteries — finding that a higher average reading during adulthood is linked with a greater risk for the two most common types of stroke.

Health Lab
Women over the age of 65 who require complex heart surgery are more likely than men to receive care at low quality hospitals — where they also die in greater numbers following the procedure, a Michigan Medicine study finds.

Health Lab
Two studies led by Michigan Medicine find that female patients who undergo heart surgery are less likely to have secondary ailments corrected during a procedure — despite guidelines that indicate they should.

Health Lab
Children with inoperable brain tumors may die sooner if they live in areas with lower average income and education levels, a Michigan Medicine-led study finds.

Health Lab
For a Michigan man in his early 30s who never expected to have a stroke so young, the quick action of others allowed him to fully recover with no need for rehabilitation.

Health Lab
Although diet is the leading contributor to premature death from heart disease in the United States, fewer than one-quarter of people who undergo major heart events receive dietary counseling in the aftermath, a study finds.
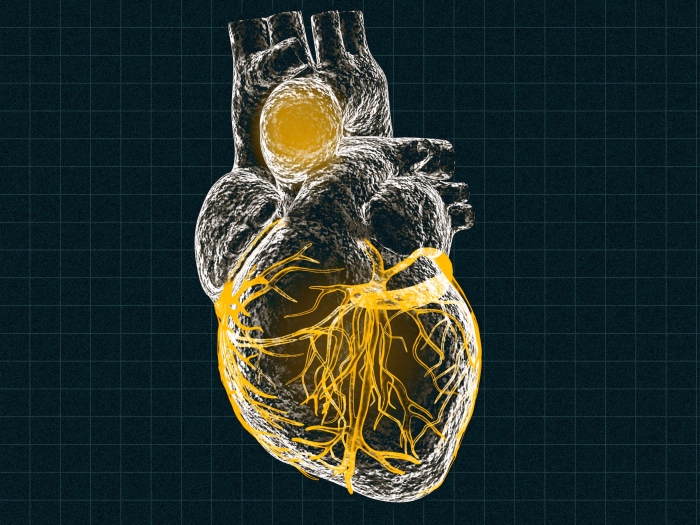
Health Lab
Using human cells in an animal body, a team of researchers has developed a functional model of thoracic aortic aneurysm, creating opportunities for more effective understanding of disease development and treatments for the potentially fatal condition.
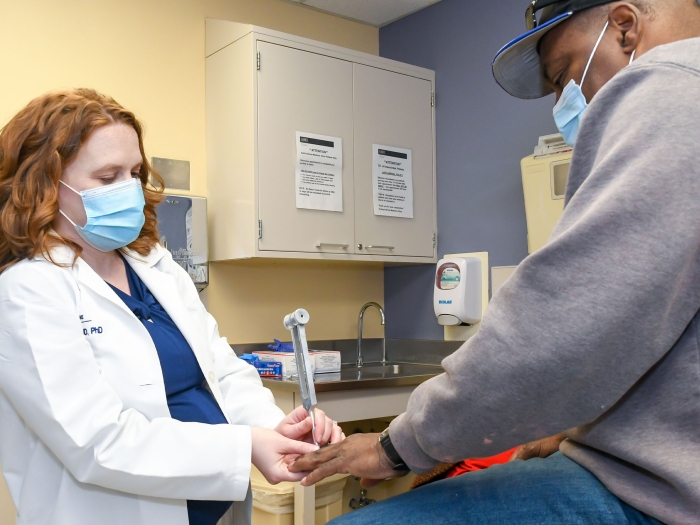
Health Lab
A research team, led by Michigan Medicine and in partnership with Hurley Medical Center, finds that nearly three-quarters of patients at a clinic in Flint, Mich., a community that is predominantly Black and socioeconomically disadvantaged, had neuropathy — of which 75% was undiagnosed.
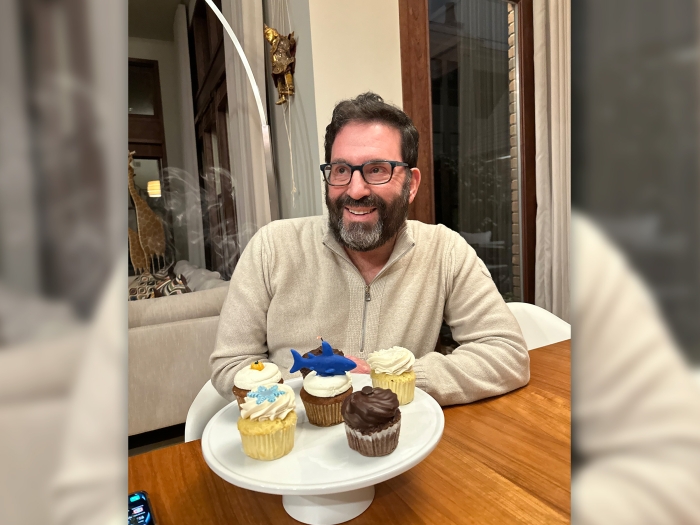

Health Lab
A patient who has received two heart transplants years apart shares his story and the importance of advocating for organ donation.

Health Lab
Researchers improved memory and reduced neuroinflammation in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s Disease, suggesting another avenue for potential treatment.
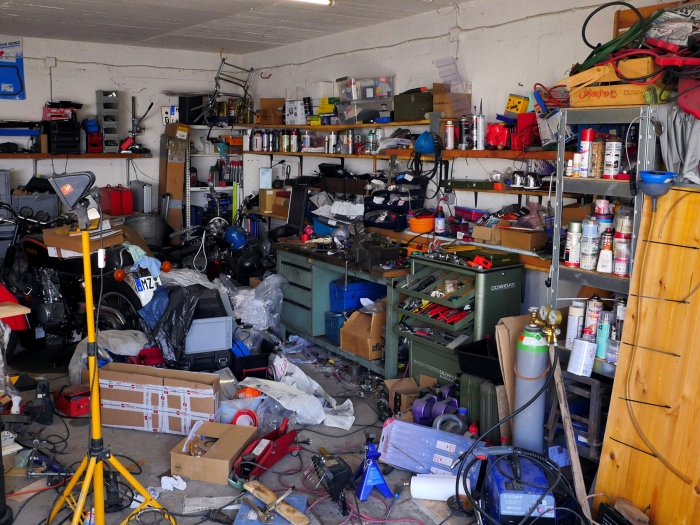

Health Lab
A Michigan Medicine study finds that storing chemicals in a garage at home may associate with an increased risk of ALS.

Health Lab
Around 10% of all deaths following percutaneous coronary intervention are potentially preventable, a study led by Michigan Medicine finds.