With use growing for treatment-resistant depression and other mental health conditions, more use of tests and contraception by patients who could become pregnant is needed, authors say
2:49 PM
Author |
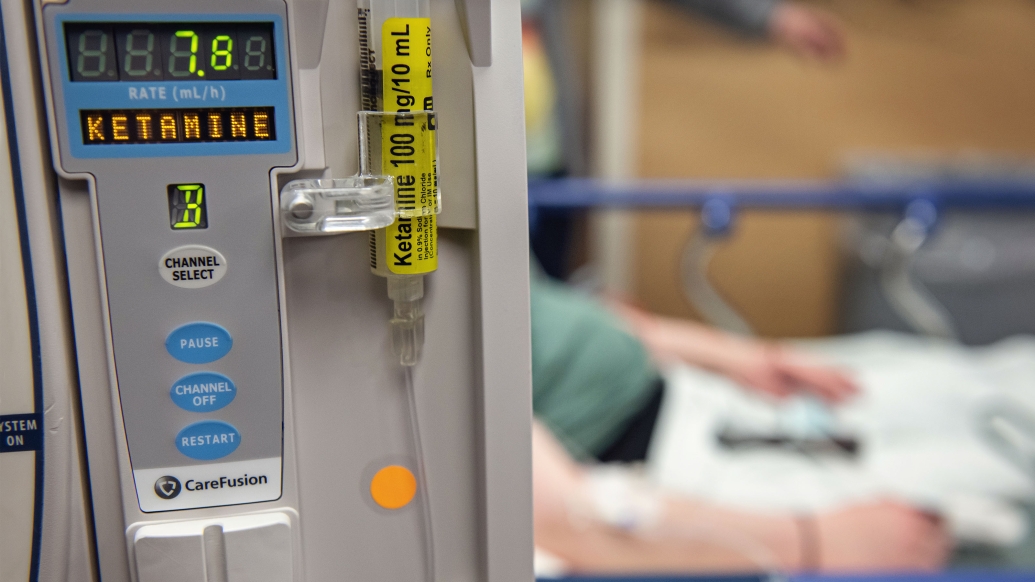
More hospitals and clinics now offer patients ketamine therapy for severe depression, post-traumatic stress disorder and other mental health conditions that haven’t responded to other treatments.
While ketamine is a safe medication when used with medical supervision, it does have a little known complication: it may be very harmful to a developing fetus.
It should not be used during pregnancy.
But a study suggests that ketamine prescribers aren’t paying enough attention to this risk and should do more to make sure that patients receiving ketamine aren’t pregnant and are aware of the need to use contraception while undergoing a course of treatment over multiple months.
The article in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry was written by researchers from the University of Michigan’s academic medical center, Michigan Medicine.
It reports the results of a survey and document review conducted of ketamine clinics nationwide, and a review of records from the ketamine clinic for depression at U-M Health.
In all, they found a wide variation in policies, practices and warnings about ketamine use related to pregnancy and reproduction.
This is despite the fact that the 119 clinics that answered the survey report treating a total of more than 7,000 patients with ketamine per month, and estimate that a third of patients they serve are female and premenopausal.
Key findings
More than 75% of responding clinics said they have a formal pregnancy screening process, but only 20% actually require a pregnancy test at least once prior to or during treatment.
More than 90% of clinics said they note that pregnancy is a contraindication to ketamine treatment in their informed consent documents and/or conversations.
But less than half of clinics reported discussing specific potential risks with patients.
The researchers also looked at informed consent documents on the websites of 70 other ketamine clinics.
In all, 39% did not include language about pregnancy in their documents, and those that did were generally vague.
SEE ALSO: When pills and talk therapy aren’t enough, these options may help
When it came to contraception counseling, only 26% of the clinics that answered the survey said they discuss the potential need for contraception with ketamine patients.
Less than 15% of the clinics specifically recommend or require contraception use during treatment.
This is especially striking, the authors say, because more than 80% of clinics reported prescribing longterm maintenance ketamine, with nearly 70% of these saying their patients receive care for more than six months and many saying patients receive ketamine for a year or more.
The review of records from 24 patients treated with ketamine at U-M’s clinic in the past showed all had taken a pregnancy test before beginning treatment and weekly during treatment, and but only half had documentation in their records that they were using contraception.
Inspiration for the study
Lead author Rachel Pacilio, M.D., a psychiatrist who recently joined Michigan Medicine as a clinical assistant professor after completing her residency at U-M Health, says the idea for the study came to her during a rotation in the perinatal psychiatry clinic.
Ketamine is a really effective, potentially lifesaving, treatment for the right patients, but not everyone is a good candidate for it. We need to ensure this treatment is being delivered in a way that benefits patients while preventing harm.”
-Rachel Pacilio, M.D.
Patients who were pregnant or had recently given birth asked her about ketamine as an option for their treatment-resistant depression.
They had heard of the potential positive impact of the drug when given intravenously as an off-label use of a common anesthetic, or as an intranasal spray of esketamine that’s marketed as Spravato and approved by the United States Food and Drug Administration.
“There was little guidance available to prescribers other than the general recommendation to avoid ketamine in patients who are pregnant, because of the unknown potential impact on a fetus or a breastfeeding newborn,” said Pacilio.
“That sparked our interest in surveying clinics to see how they were handling this during their intake processes, initial treatment courses and during the maintenance therapy phase. As far as we know, this is the first time this has been looked into.”
Variation in oversight
Clinics offering intravenous ketamine require specialized staff and post-administration monitoring for each session.
And the FDA specifically requires at least two hours of in-person observation after a dosing of intranasal Spravato to ensure safety and to monitor for complications.
By contrast, other formulations of ketamine can be administered outside the clinical setting with minimal oversight.
Some clinics surveyed reported prescribing sublingual ketamine for at-home use.
The study did not include online, direct-to-consumer ketamine providers that offer treatment exclusively via telehealth consultations.
It's unknown how these companies address reproductive and other safety concerns despite their growing popularity among patients.
“These data suggest that a large population of patients could be pregnant, or could become pregnant, while receiving ketamine treatment via multiple routes of administration. This risk increases with the duration of therapy which can last weeks for the initial course and a year or more for maintenance,” said Pacilio.
“Many patients do not know that they’re pregnant in the first weeks, and animal studies of ketamine are very concerning for potential harm to the fetus during this time.”
She notes that while many psychotropic medications have been studied extensively and found to be safe for use in pregnancy, including a variety of antidepressants, antipsychotics and other psychiatric drugs, there's no data to support the use of ketamine for psychiatric illness in pregnancy.
SEE ALSO: Ketamine’s promise for severe depression grows, but major questions remain
Pacilio points out that the FDA’s risk mitigation program for Spravato, the nasal form of ketamine, does not include any provisions about pregnancy.
A warning issued by the FDA last fall about the risks of compounded forms of ketamine available online also does not mention precautions about pregnancy.
“The variability in practice that we see among clinics in the community in this study is stark,” said Pacilio.
“The field is really in need of standardization around reproductive counseling, pregnancy testing and the recommendation for contraception during ketamine treatment.”
If someone becomes pregnant while undergoing ketamine treatment, and has to stop receiving the drug for the remainder of the pregnancy, they're at risk for a depression relapse that could continue after the baby is born.
Perinatal and postpartum depression are major risk factors for a range of issues in both the birthing parent and the infant.
Need for standard guidance
After sharing their findings about U-M patients in the study with leaders of the U-M Health ketamine clinic, Pacilio says that the clinic began recommending the use of highly reliable forms of contraception to patients who could become pregnant while receiving ketamine treatment.
Small standalone community clinics offering ketamine therapy may not have the same resources that a large clinic like U-M’s does, so standard guidance could especially benefit them.
Interventions including improved patient education with an emphasis on the requirement for pregnancy prevention for the duration ketamine treatment during the informed consent process, routine pregnancy testing before and during treatment for appropriate patients, and effective contraceptive counseling are needed.
Many of these could be easily implemented and have the potential to positively impact public health.
“Ketamine is a really effective, potentially lifesaving, treatment for the right patients, but not everyone is a good candidate for it,” she said.
“As psychiatrists, we need to ensure this treatment is being delivered in a way that benefits patients while preventing harm.”
In a commentary in the journal about the U-M team’s findings, psychiatrist and journal editor Marlene Freeman, M.D., wrote that based on the findings, “It is imperative that best practices for women of reproductive age for the use of ketamine and esketamine are determined and utilized.”
She adds that this is especially important in light of the changing landscape of abortion-related laws.
Freeman also notes that those who have used ketamine in any form during pregnancy, as well as other psychotropic medications, can join the National Pregnancy Registry for Psychiatric Medications during pregnancy and help provide much needed information on the impacts of these medications.
Additional authors: In addition to Pacilio, the study’s authors include Jamarie Geller, M.D., M.A., a psychiatry fellow at U-M, and faculty members Juan F. Lopez, M.D.; Sagar V. Parikh, M.D. and Paresh D. Patel, M.D., Ph.D.
Funding/disclosures: The study was funded by U-M Department of Psychiatry.
Paper cited: "Safe ketamine use and pregnancy: a nationwide survey and retrospective review of informed consent, counseling, and testing practices," J Clin Psychiatry. DOI:10.4088/JCP.24m15293
Sign up for Health Lab newsletters today. Get medical tips from top experts and learn about new scientific discoveries every week.
Sign up for the Health Lab Podcast. Add us wherever you listen to your favorite shows.

Explore a variety of health care news & stories by visiting the Health Lab home page for more articles.

Department of Communication at Michigan Medicine
Want top health & research news weekly? Sign up for Health Lab’s newsletters today!





