With numerous new and challenging obligations to face, the road to adulthood for kids and teens is anything but easy. Writer Helen Korneffel shares the latest findings from the C.S. Mott Children’s National Poll on Children’s Health and her own medical journey dealing with chronic disease
11:09 AM
Author |

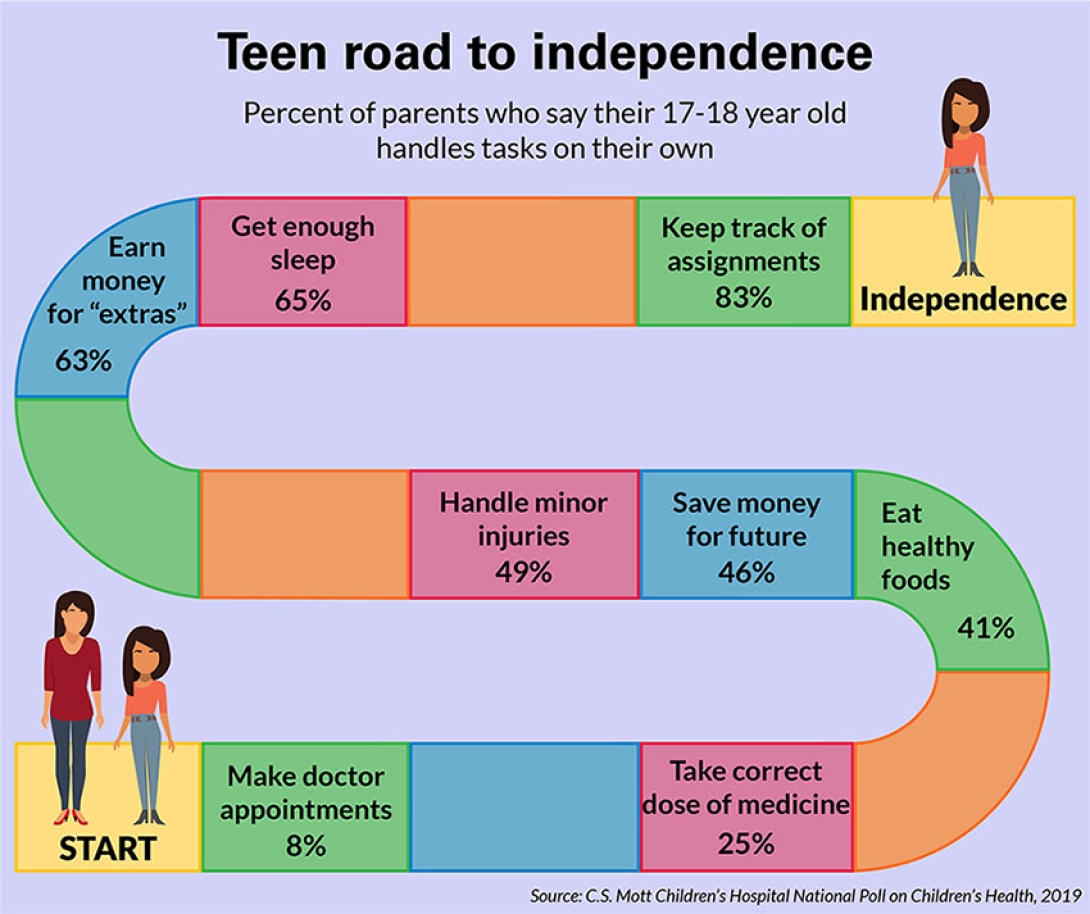
The latest University of Michigan C.S. Mott Children's Hospital National Poll on Children's Health finds that less than half of teenagers manage their own well-being, and even fewer handle health care tasks on their own.
According to the poll, nearly all parents (97%) say they are helping their teen become more independent by using strategies like allowing them to make more choices (86%), pushing them to handle tasks themselves (74%) and no longer doing things for them (65%).
LISTEN UP: Add the new Michigan Medicine News Break to your Alexa-enabled device, or subscribe to our daily updates on iTunes, Google Play and Stitcher.
Despite this, one quarter of parents surveyed say they are the main barrier to their teen's independence by not taking the time or effort to give them more responsibility.
The poll report was based on responses to questions about teen independence from a nationally representative sample of 877 parents having at least one child between the ages of 14-18 years old.
"The key to helping children and teens develop independence is to give them responsibilities early on, even at 11 or 12 years old," says Terrill Bravender, M.D., M.P.H., chief of adolescent medicine at C.S. Mott Children's Hospital.
I can speak to this from experience. As a 20-year-old old living with juvenile idiopathic arthritis, a chronic disease, I can vouch for how difficult the health care transition can be from childhood to adulthood. Like many others, my journey to independence was not a straight line.
When I was diagnosed with arthritis at 11 years old, I regularly visited pediatricians, rheumatologists, physical and occupational therapists and frequently had labs drawn. During that time I was completely dependent on my parents to handle all of the important aspects of my care, such as arranging appointments, filling out paperwork and speaking with doctors.
As I got older, I hesitantly began to take more control of my disease with their help. I slowly began to learn the names of all of my medications and speaking with my doctors at each appointment. The information I learned early on about my disease and the health care system was crucial to my success as a young adult patient living with a chronic disease.
"The adolescent transition period is a struggle even when teens don't have a chronic disease," says Bravender. "If parents are too hands off, kids never learn how to self-regulate, and if parents are too hands on, kids are too sheltered."
Sixty percent of parents polled say they view several factors as barriers to their teens becoming more independent, such as them not being mature enough (24%), not having time (22%) or not knowing enough (14%) to take on more responsibility.
Although my parents encouraged me to take control of my disease management from an early age, I did so with resentment. I was angry I had to grow up sooner than other kids my age and take on an "adult problem". Most kids do not worry about waking up in pain or struggling with walking up stairs.
MORE FROM MICHIGAN: Sign up for our weekly newsletter
Looking back, that anger was a barrier to my own health care independence before I accepted the reality and responsibilities of what it meant to live with a chronic condition, and how my parents were only trying to help me. I soon acknowledged and accepted the obstacle and decided to face it head-on.
The poll also found that parental over-involvement impedes teens from gaining experience and confidence to be independent in all aspects of their lives. The findings insist it is crucial for teens to begin taking ownership of their own health before they later face more complex, adult tasks.
Bravender recommends parents set expectations for their teens to help them learn the ins and outs of the health care world. For example, teens should be aware of what medications they are taking and their medical history by the time they are 13 years old.
To my surprise, when I entered college, many students I met had never scheduled a doctor's appointment themselves. After reading this survey, and based on my own experience, I believe parents should work together with their children and only be seen as a back-up resource when needed. Although some parents try to justify control by saying their teen is just not 'mature enough', I believe that mindset could inhibit their kid's ability to grow.
"Parents need to realize this transition period is a dialogue, not a monologue," says Bravender. "They need to start sharing responsibilities with their teen so the teen is not overwhelmed when it comes time to go off into adulthood."
Bravender adds: "If parents never let teens take responsibility, then teens will never learn. Setting up a structure for a learning environment is crucial for parents, and parents need to become comfortable with allowing natural consequences."

Explore a variety of health care news & stories by visiting the Health Lab home page for more articles.

Department of Communication at Michigan Medicine
Want top health & research news weekly? Sign up for Health Lab’s newsletters today!





