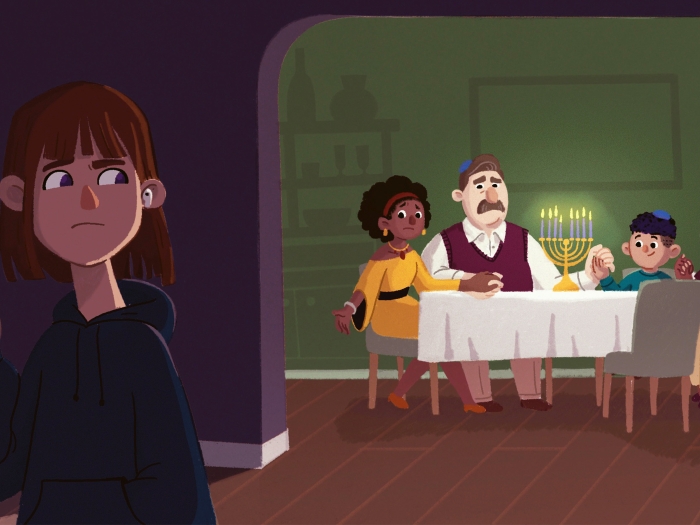
By understanding how immune response is suppressed in pregnancy, researchers pinpoint key mechanism that stops immune system from blocking cancer
5:00 AM
Author |
To understand why some cancers successfully circumvent the immune system to grow unchecked, researchers turned to pregnancy.
“In pregnancy, the immune system does not reject the growing fetus, so we know there must be mechanisms active in the placenta. In cancer, it’s the same thing: the growing tumor is not rejected by the immune system. It means the cancer cells have developed strategies to suppress immune rejection, same as in pregnancy,” said Weiping Zou, M.D., Ph.D.
It’s a good thing in pregnancy – it allows the baby to grow. But in cancer, it means the tumor grows unchecked and treatments meant to stimulate an immune response are not effective.
To understand this overlap, Zou collaborated with other researchers from the University of Michigan Health Rogel Cancer Center – bringing together unique expertise in immunology, cancer genetics, gynecologic pathology and medicinal chemistry.
They found that indeed there is a molecular mechanism shared in cancer and pregnancy that suppresses the immune system. Block this mechanism, called B7-H4, and the immune system revs up to slow cancer’s growth. Looking at mouse models and cell lines of breast and gynecologic cancers, the researchers identified the hormone progesterone as a key regulator of the B7-H4 immune checkpoint.
The paper is published in Cell.
B7-H4 expression has previously been associated with shorter survival in cancer patients. The Rogel researchers discovered that B7-H4 plays an active role in moderating the immune system in both the placenta and the tumor microenvironment.
Further, while the male hormone androgen has previously been linked to immune suppression in prostate cancer, this is the first time the female sex hormone progesterone has been shown to impact immune response in cancer.
In pregnancy, the immune system does not reject the growing fetus, so we know there must be mechanisms active in the placenta.”
--Weiping Zou, M.D., Ph.D.
Researchers used an inhibitor to block progesterone signaling in mice with breast cancer and in human breast cancer tissue samples, which did slow the cancer’s growth in mice and activated the immune response. The effect was clear but not dramatic, however.
“B7-H4 is an important checkpoint, but it’s complicated,” Zou said. “Progesterone regulation is one mechanism, but we need more studies to understand whether other mechanisms are also involved in regulating B7-H4. We do not have a direct way to block this signaling pathway. The receptors remain unknown.
“There’s something in the basic immunobiology that we still don’t understand.”
Researchers plan additional studies looking at mechanisms regulating B7-H4 protein stability, as well as the role other factors plays in cancer immunology.
Additional authors: Jiali Yu, Yijian Yan, Shasha Li, Ying Xu, Abhijit Parolia, Syed Rizvi, Weichao Wang, Yiwen Zhai, Rongxin Xiao, Xiong Li, Peng Liao, Jiajia Zhou, Karolina Okla, Heng Lin, Xun Lin, Sara Grove, Shuang Wei, Linda Vatan, Jiantao Hu, Justyna Szumilo, Jan Kotarski, Zachary T. Freeman, Stephanie Skala, Max Wicha, Kathleen R. Cho, Arul M. Chinnaiyan, Samantha Schon, Fei Wen, Ilona Kryczek, Shaomeng Wang, Lieping Chen
Funding: National Cancer Institute grants CA217648, CA123088, CA099985, CA193136, CA152470, CA46592; UTC-Yale Endowment
This work was supported by these Rogel Cancer Center Shared Resources: Immune Monitoring, Transgenic Animal Models, Cell and Tissue Imaging
Paper cited: “Progestogen-driven B7-H4 contributes to onco-fetal immune tolerance,”Cell. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2024.06.012
Sign up for Health Lab newsletters today. Get medical tips from top experts and learn about new scientific discoveries every week by subscribing to Health Lab’s two newsletters, Health & Wellness and Research & Innovation.
Sign up for the Health Lab Podcast: Add us on Spotify, Apple Podcasts or wherever you get you listen to your favorite shows.

Explore a variety of health care news & stories by visiting the Health Lab home page for more articles.

Department of Communication at Michigan Medicine

Professor
Want top health & research news weekly? Sign up for Health Lab’s newsletters today!




