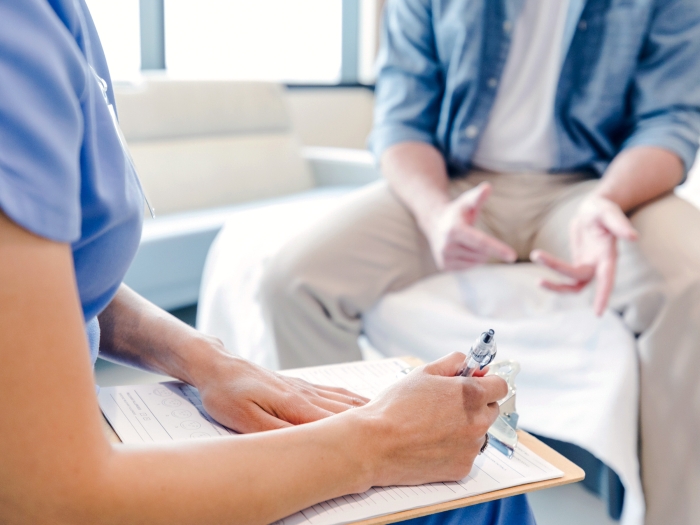
ACL injuries can leave individuals sidelined for months, if not years. An ACL expert answers patients’ top questions about the injury.
7:00 AM
Author |
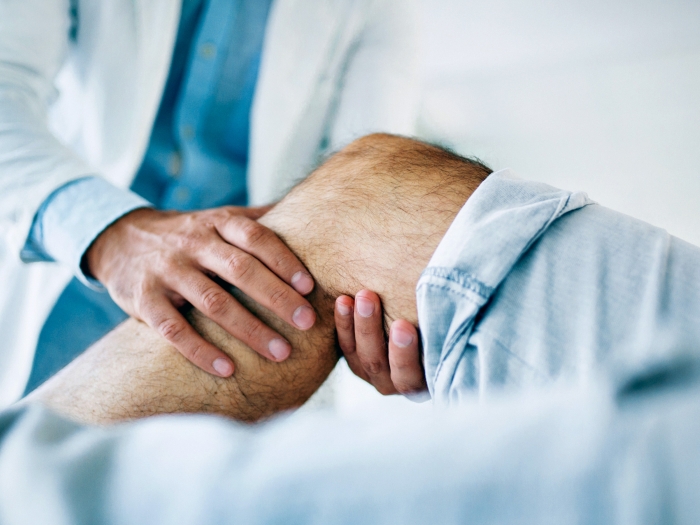
It's an injury that can leave professional and recreational athletes unable to return to the game they love.
Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injuries are caused by a sudden twisting or turning of the knee. Over 400,000 ACL injuries happen annually in the United States, with the peak age for injury being 14 years old and in females.
SEE ALSO: 5 Steps to Summer Sport Safety
Edward Wojtys, M.D., a professor of orthopedic surgery at the University of Michigan Comprehensive Musculoskeletal Center and an expert in ACL injuries, answers some of the most common questions patients have about the potentially devastating injury.
Patients want to know "Will I be able to return to this sport and how fast?" What's the typical prognosis?
Wojtys: Some ACL injuries are isolated, but some involve other tissues like the menisci or joint surfaces. When this happens, it makes the injury more difficult to treat. It really depends on the level and severity of injury.
Both recreational and competitive athletes dislike injury time because it means they are taken away from their desired activities and most emphasize their interest in getting back as quickly as possible. For physicians, this sometimes poses dilemmas because there are many uncertainties about a patient's return.
How can people know if they have an ACL injury?
Wojtys: Most patients know when they have sustained a significant injury to their knee joint, but some may not. Those who feel a lot of pain and have swelling in the knee joint usually are quite certain that something serious has happened. But some patients do not have these symptoms; they feel minor pain and after a couple of days are able to convince themselves that it's OK to try some athletic activities.
That is why the diagnosis may be confusing to a patient and clinician. The situation often requires a high index of suspicion to get it right. The truth is, some patients are very dependent upon their ACL, and when it tears they know something is wrong immediately. Other patients are not as dependent on the ligament; therefore, when it's torn, many times they function quite well, especially in activities that do not involve jumping, turning and twisting.
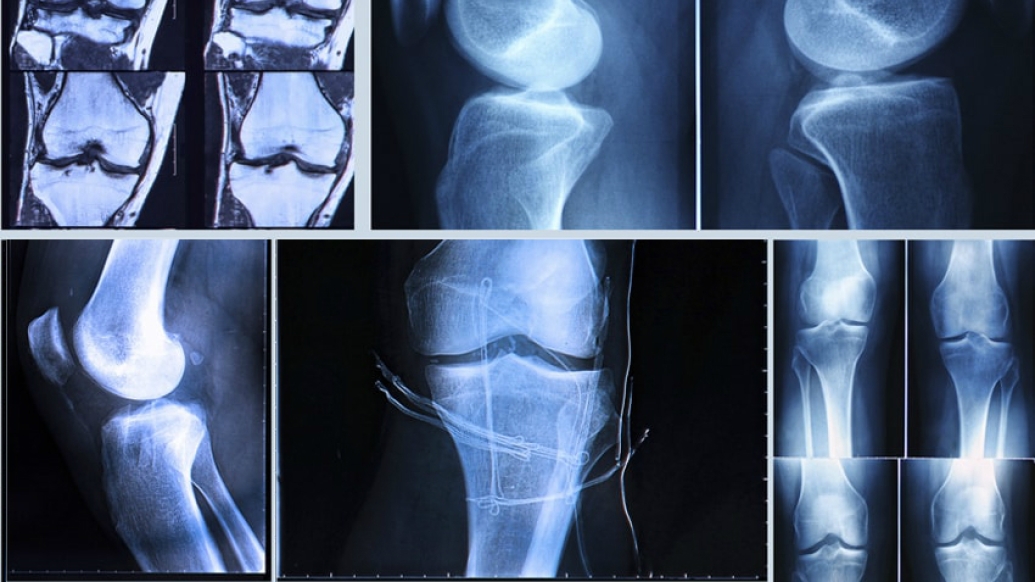
If you experience an ACL injury, what types of treatment are available?
Wojtys: Your age and activity level are important factors to consider when deciding on a treatment plan. There are some individuals who do not wish to return to running, jumping, turning or twisting activities and are more than happy to ride a bike or swim instead. For those patients, conservative treatment with rehabilitation may suffice in returning them to an active lifestyle. If, however, you wish to return to jumping, turning and twisting sports at any level, most patients will need a reconstructive operation in order to make those activities safe over the long haul.
How long does it take to recover from an ACL injury, and will a patient ever be back to normal?
Wojtys: The return to full activity after an ACL injury and/or reconstruction is highly dependent on multiple factors. Some ACL injuries are isolated and do not involve damage to other ligaments, such as the surface of the femur or tibia, or the menisci. For those patients, recovery might be much easier whether pursuing the conservative or the operative approach.
SEE ALSO: Heart Surgeon Gives New Meaning to 'Running to Work'
The ability to return to full activity is also dependent upon gaining full motion at the knee, strength, reflex activity and function. Because there are so many factors involved with the rehabilitation, it's tough to judge one's ability to return without knowing those specifics. In general, the patient's motivation is extremely important. That can overcome many factors.
If the ACL is not reconstructed, the knee will remain loose. That looseness or laxity may not be a problem if the patient eliminates jumping, twisting activities. To return safely to vigorous sports, such as basketball, soccer or football, an ACL reconstruction is usually needed.
Is there anything patients can do to avoid an ACL injury?
Wojtys: We do not understand all of the susceptibility factors at this time, but we are making progress. No doubt some structural and physical factors do increase injury risk.
There are also a number of ACL injury prevention programs available. The most successful have been the PEP Program from Santa Monaco Sports Medicine Foundation and Sportsmetrics by Cincinnati Sports Medicine. The success of these programs depends highly on the demographics of the participants and the sporting activity involved. Most programs attempt to improve limb control and positioning in hopes of avoiding hazardous positions that can cause injury.

Explore a variety of health care news & stories by visiting the Health Lab home page for more articles.

Department of Communication at Michigan Medicine
Want top health & research news weekly? Sign up for Health Lab’s newsletters today!